|
 |
 |
|
 Yunseong Lee Yunseong Lee |
 Chunghyun Lee Chunghyun Lee |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
| 6G Communication and Networking |
| As a new next-generation communication network emerges every 10 years, IMT-2030, a vision and white paper for 6G communication and networks, was recently released. In the 6G communication and network, most of the requirements are much higher than those of the existing 5G. Accordingly, in order to satisfy the requirements of the 6G along with the development of data transmission technology, a lot of research on mmWave and THz band communication, which is a more extended bandwidth, is being conducted. In addition, Innovative technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), semantic communication (SC), and integrated communication and sensing (ISAC) are being actively researched to realize ultra-reality as well as ultra-bandwidth and ultra-communication.
|
|
|
|
| Fundmental Technologies and Broader Impact |
| (1) Antenna Technology with IRS |
| (2) Multi-Access Technology |
| (3) 6G Networking Technology |
| (4) 6G Network Management Technology |
| (5) Broader Impact |
|
|
|
|
| (1) Antenna Technology with IRS |
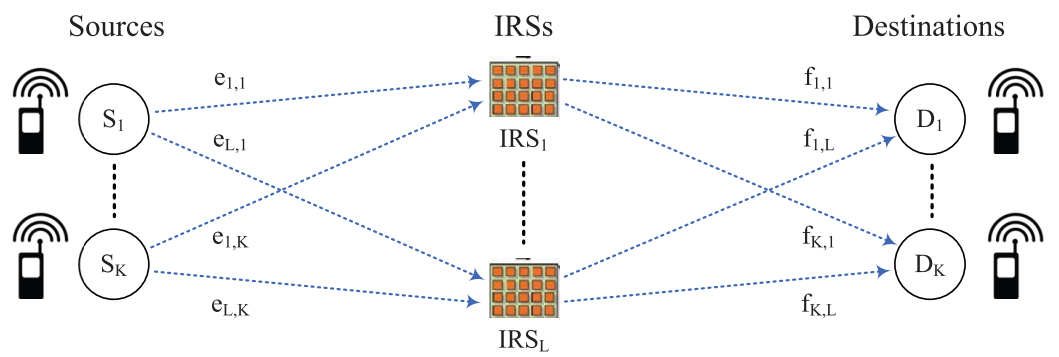
| In the current 5G frequency band, wireless communication uses only limited frequencies due to the linearity of frequency and the effect of propagation distance. This problem becomes bigger as the frequency increases in the existing 5G band. |
| As a way to solve this problem, research is being conducted on transmission technologies that are difficult to implement in the 5G/6G band, such as reflection, diffraction, polarization manipulation, and focusing of radio waves using intelligent reflective surface (IRS) technology. |
| In particular, research on beam forming technology using ultra-IRS is being conducted worldwide as a method of overcoming radio transmission loss in a 5G/6G environment. |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
| (2) Multi-Access Technology |
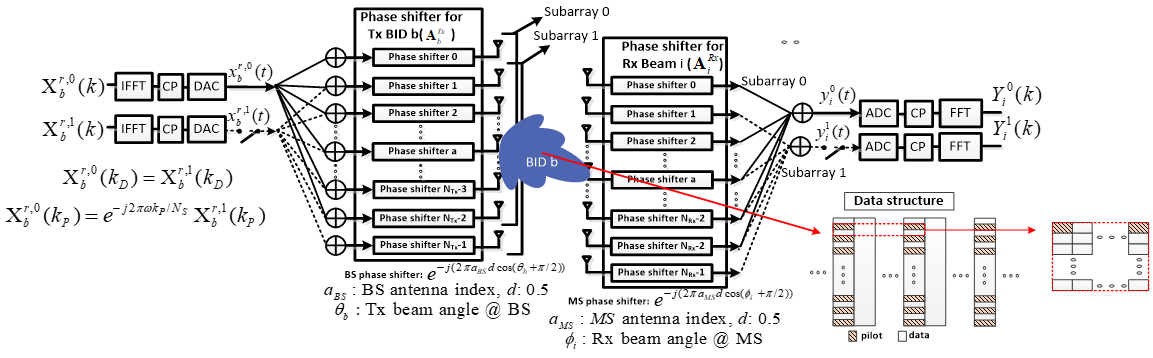
| Since 6G must provide a variety of ultra-performance services, performance indicators such as transmission speed, delay time, and number of supportable devices are innovatively increased compared to 5G. Previously, 5G targeted a transmission speed of 20 Gbps, but 6G must meet a maximum transmission speed of 1,000 Gbps and a user experience speed of 1 Gbps or more to provide services such as hologram and extended reality (XR). |
| Therefore, in 6G communication, beam training, that is, finding a pair of optimal transmission/reception beams, is an essential process for maximizing beamforming performance based on MIMO. In particular, since the beam training/tracking problem is more difficult in the 6G THz cellular communication system using IRS, fundmental technology development for multiple access technology is actively underway. |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
| (3) 6G Networking Technology |
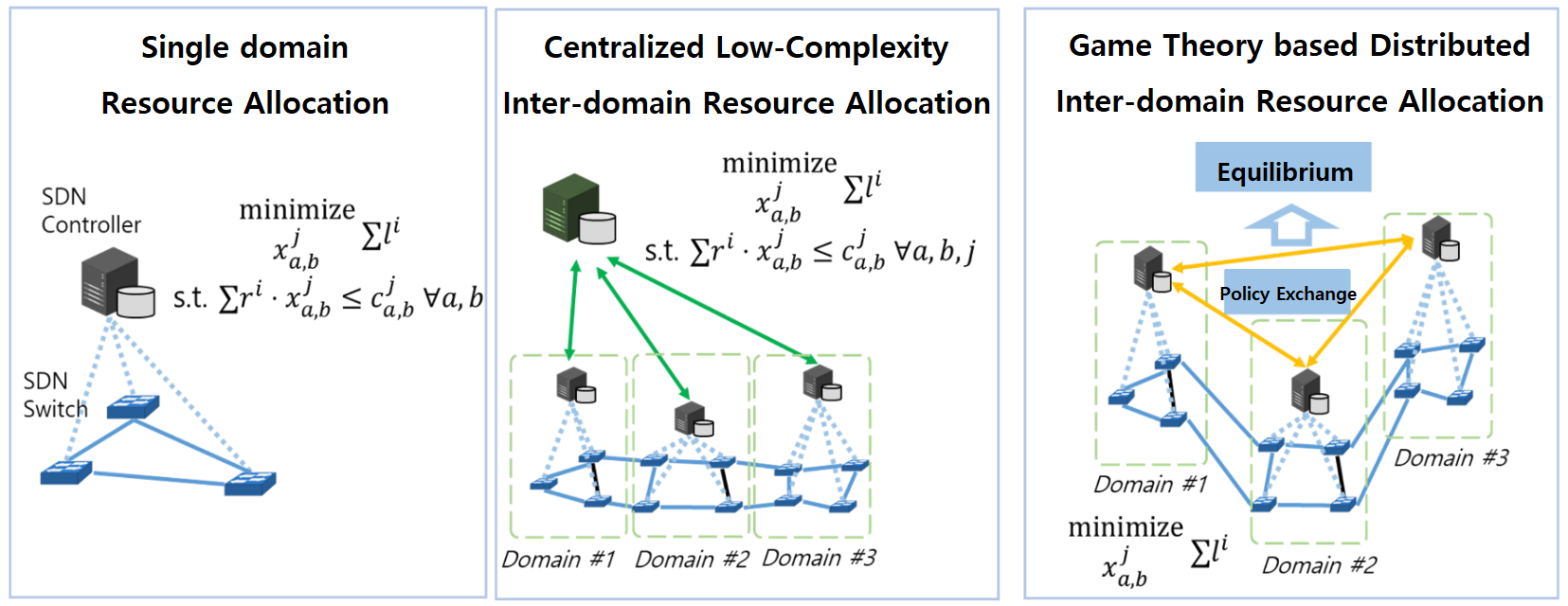
| In the 6G network, strict control of latency as well as ultra-low latency of end-to-end information transmission through the network is required for ensuring the quality of ultra-realistic services and the stability of ultra-precision services in industrial areas. |
| In addition, in order to guarantee a quality of service (QoS) for real-time service on the Internet, a technology that can flexibly respond to changes in network conditions is required. This is because the current technology has restrictions on changes in network conditions because resource management is performed in independent spaces between the network core and the wireless network section, and policy-based resource management technology is adopted. |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
| (4) 6G Network Management Technology |
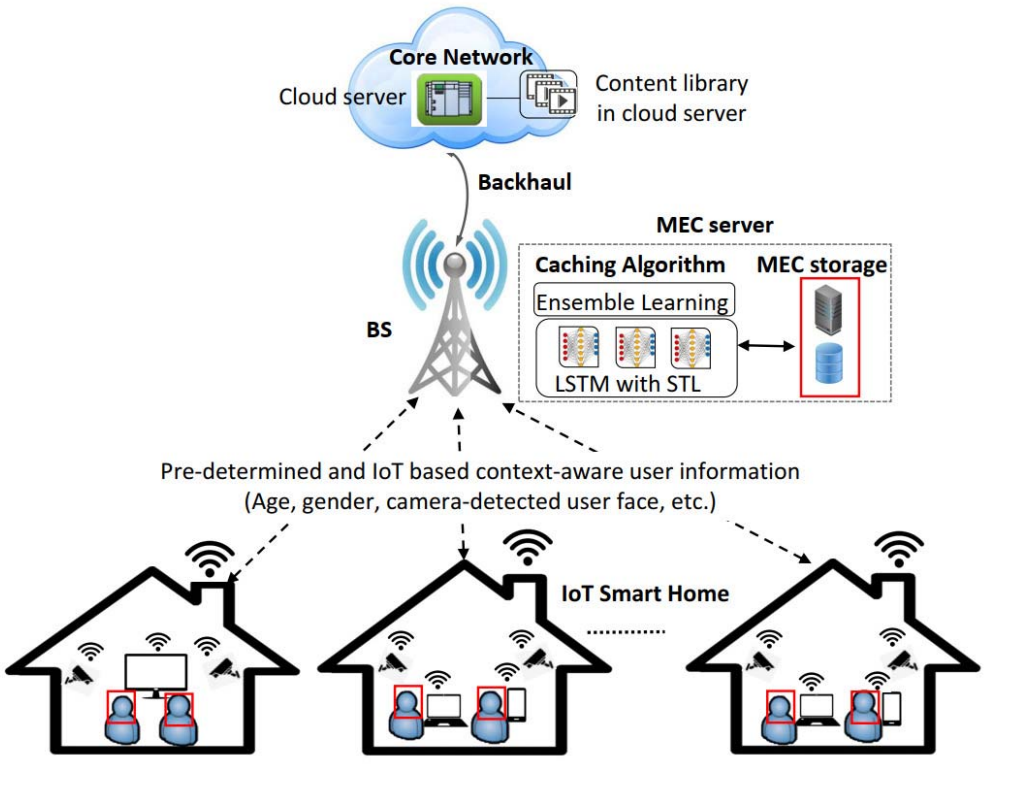
| In a 6G network environment, multiple users receive services from the server. Therefore, management technology for ultra-efficiency between server and user is required. Therefore, many studies are being conducted such as hierarchical offloading, time synchronization, on-time caching, and streaming bitrate adpatation, in order to manage the resources & server load, and to ensure quality of experience (QoE) for users. |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
| (5) Broader Impact |
| Securing 6G communication and network-based technology frees you from the scarcity of network resources, creating opportunities for the development of new types of wireless communication devices and services. In addition, it is possible to lead the global network industry market based on securing references in Korea, which has the largest and most active market among the world's smart markets. In addition, with the advancement of 6G communication and network technologies, we expect to make significant contributions to academia and industry in the future by securing expertise in core technologies in related new industries. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
D. S. Lakew, A.-T. Tran, N.-N. Dao, and S. Cho,
"Intelligent Offloading and Resource Allocation in Heterogeneous Aerial Access IoT Networks,"
IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 10, no. 7, pp. 5704-5718 April 2023.
[PDF]
[IEEE Xplore]
|
 |
T. P. Truong, V. D. Tuong, N.-N. Dao, and S. Cho,
"FlyReflect: Joint Flying IRS Trajectory and Phase Shift Design using Deep Reinforcement Learning,"
IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 4605-4620, March 2023.
[PDF]
[IEEE Xplore]
|
 |
T.-V. Nguyen, A.-T. Tran, N.-N. Dao, H. Moon, and S. Cho,
"Information Fusion on Delivery: A Survey on the Roles of Mobile Edge Caching Systems,"
Elsevier Information Fusion, vol. 89, pp. 486-509, January 2023.
[PDF]
|
 |
T.-V. Nguyen, T. P. Truong, T. M. T. Nguyen, W. Noh, and S. Cho,
"Achievable Rate Analysis of Two-Hop Interference Channel with Coordinated IRS Relay,"
IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, vol. 21, no. 9, pp. 7055-7071, September 2022.
[PDF]
[IEEE Xplore]
|
 |
N.-N. Dao, D.-N. Vu, W. Na, T.-M. Hoang, D.-T. Do, and S. Cho,
"Adaptive Bitrate Streaming in Multi-user Downlink NOMA Edge Caching Systems with Imperfect SIC,"
Elsevier Computer Networks, vol. 212, July 2022.
[PDF]
|
 |
V. D. Tuong, T. P. Truong, T.-V. Nguyen, W. Noh, and S. Cho,
"Partial Computation Offloading in NOMA-Assisted Mobile Edge Computing Systems Using Deep Reinforcement Learning,"
IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 8, no. 17, pp. 13196-13208, September 2021.
[PDF]
[IEEE Xplore]
|
 |
W. Na, S. Jang, Y. Lee, L. Park, N.-N. Dao,
and S. Cho,
"Frequency Resource Allocation and
Interference Management in Mobile
Edge Computing for an Internet of
Things System,"
IEEE Internet of Things Journal,
vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 4910-4920, June 2019.
[PDF]
[IEEE Xplore]
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|